Assumptions For Binomial Distribution | There are a fixed number of trials. Binomial distribution formula is used to calculate probability of getting x successes in the n trials of the binomial experiment which are independent and the calculation of binomial distribution can be derived by using the following four simple steps: Definition standard error distribution assumptions mass probability function. Recognize the binomial probability distribution and apply it appropriately. That's a shame because the binomial distribution is.
I) underlying assumptions ii) closed form distribution formula 3. It describes the outcome of binary scenarios, e.g. A binomial distribution can be seen as a sum of mutually independent bernoulli random variables that take value 1 in case of success of the experiment and value 0 otherwise. There are three characteristics of a binomial experiment. A binomial distribution can sometimes be used in these situations as long as the population is larger relative to the sample.
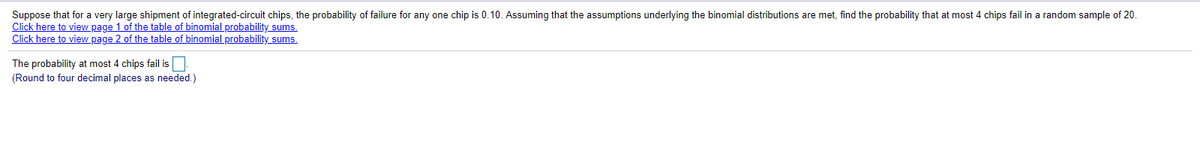
Binomial probability distributions are very useful in a wide range of problems, experiments, and surveys. It is used in a huge variety of applications such as investment modeling, a/b testing, and manufacturing process improvement (six sigma). The binomial distribution has its applications in experiments in probability subject to certain constraints. Binomial probability distributions are useful in a number of settings. Binomial distribution formula is used to calculate probability of getting x successes in the n trials of the binomial experiment which are independent and the calculation of binomial distribution can be derived by using the following four simple steps: So this is about things with two results. There is a fixed number of trials. The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. Suppose you are dealing with an experiment where: The correlated binomial is similar to moody's bet but differs from it. The number of possible outcomes depends on the number of possible successes in a. This connection between the binomial and bernoulli distributions will be illustrated in detail in the remainder of this lecture and will. Definition standard error distribution assumptions mass probability function.
More specifically, the assumptions are The random variable latexx=/latex the number of successes obtained in. However, how to know when to use them? Describes how the binomial distribution can be approximated by the standard normal distribution; Binomial distribution is a discrete distribution.

This is the currently selected item. There are fixed number of trials. I) underlying assumptions ii) closed form distribution formula 3. The binomial distribution has its applications in experiments in probability subject to certain constraints. Binomial distributions have several qualities. A binomial process in biology. Each outcome has a fixed probability, the same from trial to trial. It is well known that the underlying assumption for the binomial distribution is that there are n independent bernoulli trials. But people are less familiar with the binomial distribution. If you view this web page on a different browser (e.g., a recent version of edge. The binomial distribution is a special discrete distribution where there are two distinct complementary outcomes, a success and a failure. Each trial has only two possible outcomes denoted as success or failure. Definition standard error distribution assumptions mass probability function.
Each trial has only two outcomes. Each trial has only two possible outcomes denoted as success or failure. There are three characteristics of a binomial experiment. However, how to know when to use them? The correlated binomial is similar to moody's bet but differs from it.

The random variable latexx=/latex the number of successes obtained in. Assumptions, formula and examples with step by step solutions, what is a binomial experiment. The normal distribution is generally considered to be a pretty good approximation for hi charles, if we have to find purchase based on bellow assumption. The binomial distribution has its applications in experiments in probability subject to certain constraints. There are fixed number of trials. The experiment involves n identical trials. The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. The binomial distribution is a discrete distribution displaying data that has only two outcomes and each trial includes replacement. Only two outcomes are possible for each of n trials. Binomial distribution is a discrete distribution. The probability of success is the same for each trial. This connection between the binomial and bernoulli distributions will be illustrated in detail in the remainder of this lecture and will. The binomial distribution is given by the equation.
Assumptions For Binomial Distribution: The outcomes of each trial are independent of each other.